Somalia has long been at the epicenter of a multi-layered humanitarian crisis, pushing millions to flee.
The latest tragedy that happened with 20 Somali migrants in the Mediterranean underscores a broader pattern of migration shaped by several interlinked factors:
Key Reasons for Somali Migration
- Armed Conflict and Terrorism
Decades of civil war, along with the presence of terrorist groups like Al-Shabaab, have created an environment of persistent insecurity, forcing families to flee violence and political instability. - Extreme Poverty and Unemployment
The lack of economic opportunities, particularly for youth, drives many to seek livelihoods abroad, even if it means taking life-threatening risks. - Climate Change and Environmental Disasters
Somalia is one of the countries most affected by climate change.
Recurrent droughts, floods, and famines have displaced thousands and destroyed livelihoods, especially in rural communities. - Persecution and Human Rights Abuses
Reports of forced recruitment, gender-based violence, and suppression of freedoms push many to seek international protection.
Read also: 6 Acts of Religious Persecution in Somalia: the Hidden Truth
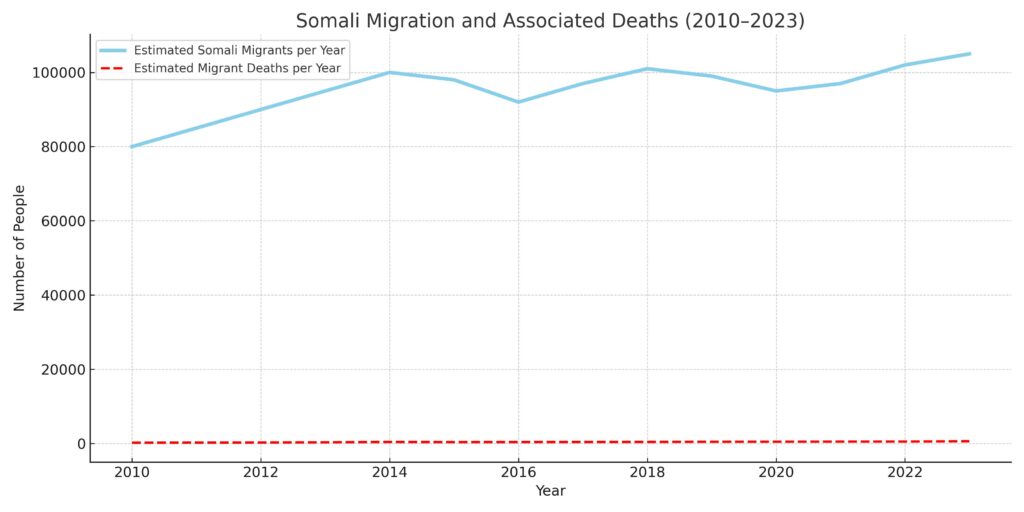
How Many Somali Migrants were Lost Since 2010?
The Mediterranean remains one of the deadliest migration routes in the world.
- According to the IOM’s Missing Migrants Project, over 28,000 people have died or gone missing while trying to cross the Mediterranean since 2014.
- Thousands of these victims are from the Horn of Africa, including Somalia.
- Tragic events like the December 2012 Gulf of Aden disaster, in which 55 Somali and Ethiopian migrants died, are not isolated.
- In 2023 alone, more than 2,500 Somali migrants are estimated to have perished on the Central Mediterranean route.
Global Response to the Somali Migration Crisis
1. Rescue and Humanitarian Assistance
Countries like Spain, Italy, and Greece have invested in maritime rescue operations, though resources remain limited and political tensions often affect coordination.
2. UN and NGO Support
The UNHCR and IOM provide critical support, including:
- Refugee status determination
- Emergency aid (shelter, food, health care)
- Voluntary return programs
3. Regional Hosting
Kenya, Ethiopia, and Yemen have hosted millions of Somali refugees over the years.
However, refugee camps like Dadaab face chronic overcrowding and funding shortages.
4. Migration Agreements and Border Policies
Europe has implemented stricter border controls and made agreements with North African countries to intercept migrants before they reach the EU—measures often criticized for prioritizing deterrence over human rights.
20 Young Somali Migrants Lost their Lives in the Mediterranean Sea
In a heartbreaking incident that highlights the perilous journey many migrants face, at least 20 Somali migrants, most of them are young people, tragically lost their lives while attempting to cross the Mediterranean Sea toward Palma Island, Spain.
The group reportedly departed from North Africa, hoping to reach European shores in search of safety, stability, and opportunity.
Only two survivors—both under the age of 18—were rescued by a passing commercial vessel after spending several days drifting without food or water.
Spanish Authorities Launches an Investigation to Uncover More Details
Emergency services in Palma confirmed that the two minors are now receiving urgent medical attention and psychological support.
Spanish authorities have launched an investigation to identify the deceased and uncover more details about the boat’s departure and the conditions that led to the tragedy.
A spokesperson for the International Organization for Migration (IOM) stated:
“This is another painful reminder of the dangers Somali migrants face when fleeing poverty, conflict, and climate instability.”
Long Term Solutions for Somali Immigration
The tragic loss of 20 Somali migrants in the Mediterranean is not just a single event—it is a symptom of a global failure to address the root causes of forced migration.
As thousands continue to risk their lives for a chance at safety and dignity, the world must shift from reactive crisis management to proactive, long-term solutions that include:
- Conflict resolution in Somalia
- Climate adaptation programs
- Safe migration pathways
- Greater international cooperation








